Basics of Waves Review
1. A single disturbance that moves from point to point through a medium is called a ___.
|
a. period
|
b. periodic wave
|
c. wavelength
|
d. pulse
|
2. If the particles of the medium are vibrating to and fro in the same direction of energy transport, then the wave is a ____ wave.
|
a. longitudinal
|
b. sound
|
c. standing
|
d. transverse
|
3. When the particles of a medium are vibrating at right angles to the direction of energy transport, then the wave is a ____ wave.
|
a. longitudinal
|
b. sound
|
c. standing
|
d. transverse
|
4. A transverse wave is traveling through a medium. See diagram below. The particles of the medium are vibrating _____.
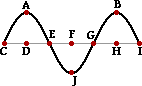
|
a. parallel to the line joining AD.
|
b. along the line joining CI.
|
|
c. perpendicular to the line joining AD.
|
d. at various angles to the line CI.
|
|
e. along the curve CAEJGBI.
|
|
5. If the energy in a longitudinal wave travels from south to north, the particles of the medium would be vibrating _____.
|
a. from north to south, only
|
b. both north and south
|
|
c. from east to west, only
|
d. both east and west
|
6. As a pulse travels though a uniform medium, the speed of the pulse ____.
|
a. decreases
|
b. increases
|
c. remains the same
|
7. The main factor which effects the speed of a sound wave is the ____.
|
a. amplitude of the sound wave
|
b. intensity of the sound
|
|
c. loudness of the sound
|
d. properties of the medium
|
|
e. pitch of the sound
|
|
8. As a wave travels into a medium in which its speed increases, its wavelength would ____.
|
a. decrease
|
b. increase
|
c. remain the same
|
9. As a wave passes across a boundary into a new medium, which characteristic of the wave would NOT change?
|
a. speed
|
b. frequency
|
c. wavelength
|
10. What is the amplitude of the wave in the diagram below?
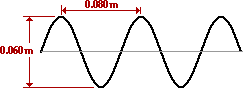
|
a. 0.03 m.
|
b. 0.04 m.
|
c. 0.05 m.
|
d. 0.06 m.
|
11. The wavelength of the wave in the diagram above (Question #10) is ____ m.
|
a. 0.030
|
b. 0.040
|
c. 0.060
|
d. 0.080
|
12. A wave d meters long passes through a medium with a speed of v meters per second. The frequency of the wave could be expressed as ____ Hz.
|
a. v / d
|
b. d / v
|
c. d•v
|
d. (d + v)
|
Consider the following diagram for Questions #13-#14.
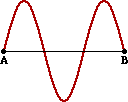
13. How many complete waves are shown in the diagram?
14. If the distance from point A to point B in the diagram is 60 cm, then the wavelength is ____.
|
a. 20 cm.
|
b. 40 cm.
|
c. 60 cm.
|
d. 90 cm.
|
15. The number of cycles of a periodic wave occurring per unit time is defined as a wave's ____.
|
a. wavelength.
|
b. period.
|
c. amplitude.
|
d. frequency.
|
16. A periodic and repeating disturbance in a lake creates waves which emanate outward from its source to produce circular wave patterns. If the frequency of the source is 2.00 Hz and the wave speed is 5.00m/s then the distance between adjacent wave crests is ___ meter.
|
a. 0.200
|
b. 0.400
|
c. 1.25
|
d. 2.50
|
e. 10.0
|
17. What is the frequency of a wave that has a speed of 0.4 m/s and a wavelength of 0.020 meter?
|
a. 10 hertz.
|
b. 20 hertz.
|
c. 0.008 hertz.
|
d. 0.5 hertz.
|
18. Many wave properties are dependent upon other wave properties. Yet, one wave property is independent of all other wave properties. Which one of the following properties of a wave is independent of all the others?
|
a. wavelength
|
b. frequency
|
c. period
|
d. velocity
|
|
19. A pendulum makes exactly 40 vibrations in 20.0 s. Its period is ____. (Be cautious of the units.)
|
a. 0.500 Hz.
|
b. 0.500 s.
|
c. 2.00 Hz.
|
d. 2.00 s.
|
e. 8.00 x 102 Hz.
|
20. A period of 0.005 seconds would be equivalent to a frequency of ____ Hz.
|
a. 20
|
b. 50
|
c. 200
|
d. 500
|
e. 2000
|
21. TRUE or FALSE:
The number of waves generated per second by a source is called the frequency of the source.
22. TRUE or FALSE:
The SI unit for frequency is hertz.
23. TRUE or FALSE:
Doubling the frequency of a wave source (without altering the medium) doubles the speed of the waves.
24. If the frequency of a wave is doubled and if the speed remains constant, its wavelength is ____.
|
a. quartered.
|
b. halved.
|
c. unchanged.
|
d. doubled.
|
25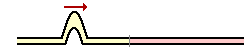 . Two different ropes with different mass densities are attached to each other. A pulse is introduced into one end of the rop and approaches the boundary as shown at the right. At the boundary, a portion of the energy is transmitted into the new medium and a portion is reflected. Which one of the diagrams below depicts the possible location and orientation of the pulse shortly after the incident pulse reaches the boundary?
. Two different ropes with different mass densities are attached to each other. A pulse is introduced into one end of the rop and approaches the boundary as shown at the right. At the boundary, a portion of the energy is transmitted into the new medium and a portion is reflected. Which one of the diagrams below depicts the possible location and orientation of the pulse shortly after the incident pulse reaches the boundary?
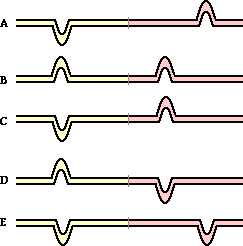
26. When a pulse reaches a boundary between two different media, it will be____.
|
a. reflected, only.
|
b. transmitted, only.
|
|
c. partly reflected and partly transmitted.
|
d. neither reflected nor transmitted.
|
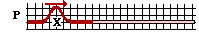
27. Diagram P at the right shows a transverse pulse traveling along a dense rope toward its junction with a less dense rope. Which of the diagrams (A, B, C, D, or E) below depicts the ropes at the instant that the reflected pulse again passes through its orignal position marked X? Consider such features as amplitude and relative speed (i.e., the relative distance of the transmitted and reflected pulses from boundary).
28. A wave whose speed in a snakey is 4.4 m/s enters a second snakey. The wavelength changes from 2.0 m to 3.0 m. The wave in the second snakey travels at approximately ____.
|
a. 1.5 m/s.
|
b. 2.2 m/s.
|
c. 2.9 m/s.
|
d. 4.4 m/s.
|
e. 6.6 m/s.
|
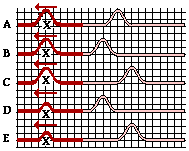
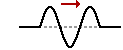 29. The diagram at the right shows a disturbance moving through a rope towards the right. If this disturbance meets a similar disturbance moving to the left, then which one of the diagrams below depict a pattern which could NEVER appear in the rope?
29. The diagram at the right shows a disturbance moving through a rope towards the right. If this disturbance meets a similar disturbance moving to the left, then which one of the diagrams below depict a pattern which could NEVER appear in the rope?
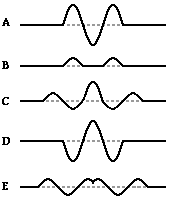
30. A 2.0-meter long rope is hanging vertically from the ceiling and attached to a vibrator. A single pulse is observed to travel to the end of the rope in 0.50 s. What frequency should be used by the vibrator to maintain three whole waves in the rope?
|
a. 0.75 Hz
|
b. 1.3 Hz
|
c. 4.0 Hz
|
d. 6.0 Hz
|
e. 8.0 Hz
|
31. A Standing wave experiment is performed to determine the speed of waves in a rope. The standing wave pattern shown below is established in the rope. The rope makes exactly 90 complete vibrational cycles in one minute. The speed of the waves is ____ m/s.
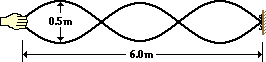
|
a. 3.0
|
b. 6.0
|
c. 180
|
d. 360
|
e. 540
|
32. Consider the standing wave pattern shown below. A wave generated at the left end of the medium undergoes reflection at the fixed end on the right side of the medium. The number of antinodes in the diagram is _____.
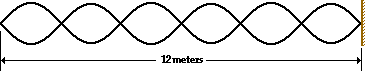
|
a. 3
|
b. 5
|
c. 6
|
d. 7
|
e. 12
|
33. A node is a point located along the medium where there is always ______.
|
a. a double crest
|
b. a double trough
|
c. constructive interference
|
|
d. destructive interference
|
e. a double rarefaction
|
|
34. TRUE or FALSE:
Constructive interference of waves occurs when two crests meet.
35. Which phenomenon is produced when two or more waves passing simultaneously through the same medium meet up with one another?
|
a. refraction
|
b. diffraction
|
c. interference
|
d. reflection
|
36. 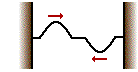 Two pulses are traveling in opposite directions along the same medium as shown in the diagram at the right. Which diagram below best depicts the appearance of the medium when each pulse meets in the middle?
Two pulses are traveling in opposite directions along the same medium as shown in the diagram at the right. Which diagram below best depicts the appearance of the medium when each pulse meets in the middle?
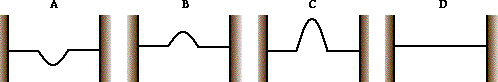
37. TRUE or FALSE:
A vibrating object is necessary for the production of sound.
38. Which one of the following CANNOT transmit sound?
|
a. Liquid air
|
b. Gaseous oxygen
|
c. Liquid water
|
|
d. Solid steel
|
e. Perfect vacuum
|
|
Navigate to:
Review Session Home - Topic Listing
Waves - Home || Printable Version || Questions with Links
Answers to Questions: All || #1-#14 || #15-#26 || #27-#38
You Might Also Like ...
Users of The Review Session are often looking for learning resources that provide them with practice and review opportunities that include built-in feedback and instruction. If that is what you're looking for, then you might also like the following:
- The Calculator Pad
The Calculator Pad includes physics word problems organized by topic. Each problem is accompanied by a pop-up answer and an audio file that explains the details of how to approach and solve the problem. It's a perfect resource for those wishing to improve their problem-solving skills.
Visit: The Calculator Pad Home | Calculator Pad - Vibrations and Waves
- Minds On Physics the App Series
Minds On Physics the App ("MOP the App") is a series of interactive questioning modules for the student that is serious about improving their conceptual understanding of physics. Each module of the series covers a different topic and is further broken down into sub-topics. A "MOP experience" will provide a learner with challenging questions, feedback, and question-specific help in the context of a game-like environment. It is available for phones, tablets, Chromebooks, and Macintosh computers. It's a perfect resource for those wishing to refine their conceptual reasoning abilities. Part 5 of the series includes topics on Wave Motion.
Visit: MOP the App Home || MOP the App - Part 5