Reflection and Mirrors Review
Navigate to:
Review Session Home - Topic Listing
Reflection and Mirrors - Home || Printable Version || Questions with Links
Answers to Questions: All || #1-#19 || #20-#26 || #27-#32 || #33-#42
Part C: Calculations and Explanations
33. Distinguish between diffuse and regular (specular) reflection in terms of both cause and result.
|
Answer:
Specular (or regular) reflection occurs when light reflects off a microscopically smooth surface. Light rays which are incident within a beam will reflect and remain in the beam.
Diffuse reflection occurs when light reflects off a microscopically rough surface. Light rays which are incident in a beam will diffuse (or scatter) and reflect in a variety of directions.
In each case the law of reflection holds; in diffuse reflection, the normals for each individual ray are not oriented in the same direction.
|
34. Write the formulae which show the relationship between image distance, object distance and focal length, and the magnification of an object/image.
|
Answer:
Please know this one:
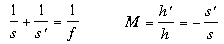
where s and h stand for object distance and object height,
and s' and h' stand for image distance and image height,
and f stands for focal length,
and M stands for magnification.
|
35. Fill in the blanks below for the problem-solving rules:
Focal lengths, object and image distances are ________ if they are on the reflective side of the mirror. Object and image heights are positive if they are ________ the principle axis.
|
Answer:
Focal lengths, object and image distances are positive if they are on the reflective side of the mirror. Object and image heights are positive if they are below the principle axis.
The do and di values (s and s') and the ho and hi values (h and h') can have positive and negative values associated with them. In physics, a + or - in front of a quantity is always descriptive of some physical feature. In ray optics, a + distance (do, di or f) means in front of the mirror as the object; a negative distance means behind the mirror. A + height means above the principal axis and a - height means below the principal axis.
|
36. What is the focal length of a mirror which gives an image 3.00 meters away when an object is placed 150. cm from it?
|
Answer: 100. cm or 1.00 m
Use the mirror equation:
1/di + 1/do = 1/f
where di = +300. cm and do = +150. cm. (Note: since di > do, it must be a concave mirror and the image must be real.)
Substitute and solve for f.
1/(150. cm) + 1/(300. cm) = 1/f
1/f = 3.00/(300. cm) or 0.0100/cm
f = 100. cm = 1.00 m
|
37. Where is the image located when an object is placed 60.0 cm from a mirror which has a focal length of 20.0 cm?
|
Answer: 30.0 cm
Use the mirror equation:
1/di + 1/do = 1/f
where d0 = +60.0 cm and f = +20.0 cm.
Substitute and solve for di.
1/(60.0 cm) + 1/di = 1/(20.0 cm)
1/di = 1/(20.0 cm) - 1/(60.0 cm) = 2/(60.0 cm)
di = 30.0 cm
|
[ #33 | #34 | #35 | #36 | #37 | #38 | #39 | #40 | #41 | #42 ]
38. How far would an object need to be placed from a mirror of focal length 10.0 cm if it is to produce an image which is 20.0 cm BEHIND the mirror?
|
Answer: 6.67 cm
Use the mirror equation:
1/di + 1/do = 1/f
where di = -20.0 cm and f = +10.0cm.
Substitute and solve for do.
1/do + 1/(-20.0 cm) = 1/(10.0 cm)
1/do = 1/(10.0 cm) - 1/(-20.0 cm) = 3.00/(20.0 cm) = 0.150/cm
do = 6.67 cm
|
39. A mirror with a focal length of -100. cm is used to form an image. An object is placed 50.0 cm in front of the mirror.
a. Where is the image located?
b. What type of mirror is being used in this problem?
|
Answer: -33.3 cm; convex mirror
Use the mirror equation:
1/di + 1/do = 1/f
where d0 = +50.0 cm and f = -100. cm. (Note: this is a convex mirror since the focal length is negative.)
Substitute and solve for di.
1/(50.0 cm) + 1/di = 1/(-100. cm)
1/di = 1/(-100. cm) - 1/(50.0 cm) = -3.00/(100. cm) or -0.03/cm
di = -33.3 cm
|
40. An object is placed 20 cm from a mirror of focal length 10.0 cm. The object is 5.0 cm tall. Where is the image located? How tall is the image?
|
Answer: di = 20.0 cm; hi = -5.0 cm
Use the mirror equation:
1/di + 1/do = 1/f
where d0 = +20.0 cm and f = 10.0 cm.
Substitute and solve for di.
1/(20.0 cm) + 1/di = 1/(10.0 cm)
1/di = 1/(10.0 cm) - 1/(20.0 cm) = 1/(20.0 cm) or 0.0500/cm
di = 20.0cm
Use the magnification ratio to solve for hi:
hi/ho = -di/do
where ho = 5.0 cm.
hi /(5.0 cm) = - (20.0 cm)/(20.0 cm)
hi = - [(20.0 cm)/(20.0 cm)]•(5.0 cm)
hi = -5.0 cm
|
41. A 20.0 cm tall object produces a 40.0 cm tall real image when placed in front of a curved mirror with a focal length of 50.0 cm. Determine the place that the object must be located to produce this image.
|
Answer: 75 ,.0cm
Given: ho = 20.0 cm, hi = -40.0 cm, f = 50.0 cm (Note: hi is negative since the image is real.)
Strategy: use the object and image height values with the magnification ratio in order to generate an expression for di in terms of do. Then substitute the expression into the mirror equation to solve for the object distance.
hi/ho = -di/do
(-40.0 cm)/(20.0 cm) = -di/do
-2.00 = = -di/do
di = 2.00*do
Now substitute this expression into the mirror equation.
1/do+ 1/(2.00*do) = 1/(50.0 cm)
2/(2.00*do) + 1/(2do) = 1/(50.0 cm)
3/(2.00*do) = 1/(50.0 cm)
2.00*do= 150. cm
do = 75.0 cm
|
42. A mirror is used to produce a virtual image that is 5.00 times bigger than the object. If the focal length of the mirror is 100. cm, where will the image be located?
|
Answer: -400. cm
Given: M = +5.00 , f = 100. cm (Note: M is positive since the image is virtual.)
Strategy: use the magnification value with the magnification ratio in order to generate an expression for do in terms of di. Then substitute the expression into the mirror equation to solve for the object distance.
M = hi/ho = -di/do
+5.00 = -di/do
do = = -di/5.00
Now substitute this expression into the mirror equation.
1/(-di/5.00)+ 1/(di) = 1/(100. cm)
-5.00/(di) + 1/(di) = 1/(100. cm)
-4.00/(di) = 1/(100. cm)
di = -400. cm
|
Navigate to:
Review Session Home - Topic Listing
Reflection and Mirrors - Home || Printable Version || Questions with Links
Answers to Questions: All || #1-#19 || #20-#26 || #27-#32 || #33-#42
You Might Also Like ...
Users of The Review Session are often looking for learning resources that provide them with practice and review opportunities that include built-in feedback and instruction. If that is what you're looking for, then you might also like the following:
- The Calculator Pad
The Calculator Pad includes physics word problems organized by topic. Each problem is accompanied by a pop-up answer and an audio file that explains the details of how to approach and solve the problem. It's a perfect resource for those wishing to improve their problem-solving skills.
Visit: The Calculator Pad Home | Calculator Pad - Reflection and Mirrors
- Minds On Physics the App Series
Minds On Physics the App ("MOP the App") is a series of interactive questioning modules for the student that is serious about improving their conceptual understanding of physics. Each module of the series covers a different topic and is further broken down into sub-topics. A "MOP experience" will provide a learner with challenging questions, feedback, and question-specific help in the context of a game-like environment. It is available for phones, tablets, Chromebooks, and Macintosh computers. It's a perfect resource for those wishing to refine their conceptual reasoning abilities. Part 6 of the series includes topics in Reflection and Mirrors.
Visit: MOP the App Home || MOP the App - Part 6