Newton's Laws: Extra Problems
The problems below are provided as additional problems to
the original set of 30 Newton's Laws problems. Just like problems in the original set, these problems consist of a problem, an answer (revealed by clicking a link), an audio guided solution, and links to an
Overview page of formulas and to The Physics Classroom Tutorial pages. The Extra Problems pertain to various aspects of the topic of force, acceleration, free-body diagrams, and Newton's second law of motion. The problems are divided into three separate sets of problems.
Problem Set A
Problem 1:
What net force (in Newtons) would be required to give a mass of 80.5 kg an acceleration of 10.1 m/s/s?
View Audio Guided Solution.
Problem 2:
A net force of 90.7-Newtons will cause a mass of 13.1-kg to accelerate at a rate of ____ m/s/s.
View Audio Guided Solution.
Problem 3:
A net force of 805-Newtons will cause an object to have an acceleration of 15.1 m/s/s. Determine the mass of the object (in kg).
View Audio Guided Solution.
Problem 4:
Suppose that a net force F gives an object with a mass of m an acceleration of 10.1 m/s/s. If the net force were increased by a factor of 7, then the new acceleration would be ____ m/s/s.
View Audio Guided Solution.
Problem 5:
Suppose that a net force F gives an object with a mass of m an acceleration of 50.3 m/s/s. If the mass were increased by a factor of 12, then the new acceleration would be ____ m/s/s.
View Audio Guided Solution.
Problem 6:
Suppose that a net force F gives an object with a mass of m an acceleration of 100.6 m/s/s. If the net force were increased by a factor of 5.04, and the mass were increased by a factor of 9, then the new acceleration would be ____ m/s/s.
View Audio Guided Solution.
Problem 7:
Suppose that a net force F gives an object with a mass of m an acceleration of 100.2 m/s/s. If the net force were decreased by a factor of 6, and the mass were decreased by a factor of 9, then the new acceleration would be ____ m/s/s.
View Audio Guided Solution.
Problem 8:
If an object weighs 604 Newtons on Earth, then its mass is ____ kg.
View Audio Guided Solution.
Problem 9:
Determine the weight (in Newtons) of a 100.8-kg object on planet Earth.
View Audio Guided Solution.
Problem 10:
The acceleration of gravity on planet X is 20.1 m/s/s. If an object weighs 806 Newtons on Earth, then its mass on planet X would be ____ kg.
View Audio Guided Solution.
Problem 11:
The acceleration of gravity on planet Y is 25.2 m/s/s. If an object has a mass of 99.8 kg, then its weight on planet Y would be ____ N.
View Audio Guided Solution.
Problem 12:
Determine the acceleration (in m/s/s) of a 40.3-N object which experiences a net force of 149.3 N.
View Audio Guided Solution.
Problem 13:
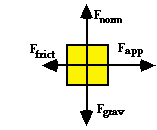 Determine the net force (in Newtons) acting upon the object whose force diagram is depicted at the right. The values of the individual forces are: Fgrav = Fnorm = 60.5 N; Fapp = 40.2 N; Ffrict = 5.7 N.
Determine the net force (in Newtons) acting upon the object whose force diagram is depicted at the right. The values of the individual forces are: Fgrav = Fnorm = 60.5 N; Fapp = 40.2 N; Ffrict = 5.7 N.
View Audio Guided Solution.
Problem 14:
(Referring to the previous problem.) Determine the horizontal acceleration (in m/s/s) of the object.
View Audio Guided Solution.
Problem 15:
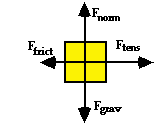 Determine the net force (in Newtons) acting upon the object whose force diagram is depicted at the right. The values of the individual forces are: Fgrav = Fnorm = 25.1 N; Ftens = 59.4 N; Ffrict = 12.2 N.
Determine the net force (in Newtons) acting upon the object whose force diagram is depicted at the right. The values of the individual forces are: Fgrav = Fnorm = 25.1 N; Ftens = 59.4 N; Ffrict = 12.2 N.
View Audio Guided Solution.
Problem 16:
(Referring to the previous problem.) Determine the horizontal acceleration (in m/s/s) of the object.
View Audio Guided Solution.
Problem 17:
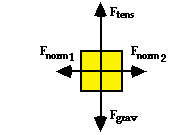 A 602-kg elevator is rising up an elevator shaft and approaching its destination. See diagram at right. The following force values are known: Ftens = 5022 N; Fnorm1 = Fnorm2 = 140 N. Determine the acceleration (in m/s/s) of the elevator.
A 602-kg elevator is rising up an elevator shaft and approaching its destination. See diagram at right. The following force values are known: Ftens = 5022 N; Fnorm1 = Fnorm2 = 140 N. Determine the acceleration (in m/s/s) of the elevator.
View Audio Guided Solution.
Problem 18:
A 85.3-kg vertically-falling skydiver experiences an upward force of air resistance of 1457 N. Determine the acceleration (in m/s/s) of the skydiver. (Enter a - value if the direction is downward.)
View Audio Guided Solution.
Problem 19:
A 1204-kg car is moving rightward at 40.2 m/s when it starts to skid to a stop. It encounters a force of friction of 9027 N. Determine the acceleration (in m/s/s) of the car.
View Audio Guided Solution.
Problem 20:
(Referring to the previous problem.) What is the distance (in meters) that the car skids before it finally stops?
View Audio Guided Solution.
Problem Set B
Problem 1:
A small model rocket is launched vertically into the air. The rocket has a mass of 0.147 kg and there is an upward thrust of 2.9136 N. What is the acceleration (in m/s/s) of the rocket?
View Audio Guided Solution.
Problem 2:
A 7.19-kg bucket suspended by a rope accelerates upwards at a rate of 3.73 m/s/s. Determine the tension (in Newtons) in the rope which pulls on the string.
View Audio Guided Solution.
Problem 3:
A 20.2-N horizontal force is applied to a 0.075-kg hockey puck to accelerate it across the ice from an initial rest position. Ignore friction and determine the final speed (in m/s) of the puck after being pushed for a time of 0.071 seconds.
View Audio Guided Solution.
Problem 4:
What upward tension force (in Newtons) would allow a 1189-kg elevator to accelerate downwards (i.e., negative) at a rate of 3.66 m/s/s?
View Audio Guided Solution.
Problem 5:
A 4.47-kg bucket suspended by a rope is accelerated upwards from an initial rest position. If the tension in the rope is 83.8 Newtons, then determine the speed (in m/s) of the bucket after 1.61 seconds.
View Audio Guided Solution.
Problem 6:
A 7.89-kg bucket of water is raised from a well by a rope attached to the bucket. If the upward acceleration of the bucket is 0.692 m/s/s, find the force (in Newtons) exerted on the bucket by the rope.
View Audio Guided Solution.
Problem 7:
A shopper in a supermarket pushes a loaded cart with a horizontal force of 16.6 Newtons. If the cart has a mass of 34 kg, how far (in meters) will it move in 3.43 seconds, starting from rest? (Ignore friction.)
View Audio Guided Solution.
Problem 8:
(Referring to the previous problem.) How far (in meters) will the cart move in the 3.43 second interval if the shopper places her 29.7-N child in the cart before she begins to push it?
View Audio Guided Solution.
Problem 9:
A 0.152-kg baseball moving at 29.3 m/s strikes the glove of a catcher. The glove recoils a distance of 12.19 cm. What is the average force (in Newtons) applied on the ball by the glove?
View Audio Guided Solution.
Problem 10:
(Referring to the previous problem.) What is the average force (in Newtons) applied on the glove by the ball?
View Audio Guided Solution.
Problem 11:
A 63.8-Newtons rightward force is applied to a 8.87-kg crate to accelerate it from rest across a horizontal surface. If the crate experiences a friction force of 47.9 Newtons, then determine the acceleration (in m/s/s).
View Audio Guided Solution.
Problem 12:
What applied force (in Newtons) would be required to give a 16.14-kg object an acceleration of 2.07 m/s/s if the force of friction opposing it is 77.7 Newtons?
View Audio Guided Solution.
Problem 13:
A 7.66-kg object experiences a horizontal acceleration of 3.33 m/s/s when a 91-N force is exerted upon it. Determine the force of friction (in Newtons) which opposes this object's motion.
View Audio Guided Solution.
Problem 14:
A train has a mass of 6.37x104 kg and is moving with a speed of 94.8 km/hr. The engineer applies the brakes which results in a net backward force of 2.45x105 Newtons on the train. The brakes are held for 3.4 seconds. How far (in meters) does the train travel during this time?
View Audio Guided Solution.
Problem 15:
A 2.25 kg mass starts from rest and slides down an inclined plane 84.4 cm long in 0.659 seconds. What is the net force (in Newtons) along the incline acting on the mass?
View Audio Guided Solution.
Problem Set C
Problem 1:
A hockey puck is hit on a frozen lake and starts moving with a velocity of 10.4 m/s. After 6.52 seconds, its velocity is 4.51 m/s. What is the magnitude of the average acceleration (in m/s/s) of the puck? Calculate your answer accurate to the third decimal place.
View Audio Guided Solution.
Problem 2:
(Referring to the previous problem.) What is the average value of the coefficient of friction between the puck and the ice? Calculate your answer accurate to the fourth decimal place.
View Audio Guided Solution.
Problem 3:
(Referring to the previous problem.) How far (in meters) does the puck travel during this 6.52 second time interval?
View Audio Guided Solution.
Problem 4:
The parachute on a race car of weight 7811 N opens at the end of a quarter-mile run when the car is traveling 35.1 m/s. What total retarding force (in Newtons) would be required to stop the car in 80.0 meters?
View Audio Guided Solution.
Problem 5:
A 2513-Newton bobsled leaves a horizontal track with a speed of 27.5 m/s. It then moves onto a horizontal track lightly sprinkled with sawdust and comes to a stop in a distance of 126 meters. What is the coefficient of kinetic friction between the runners of the sled and the sawdust-covered surface? Calculate your answer accurate to the third decimal place.
View Audio Guided Solution.
Problem 6:
Claire deAisles applies a horizontal force to push a 34.5-kg supermarket crate at a constant speed of 1.07 m/s. If the coefficient of friction between the crate and the floor is 0.371, then determine the force (in Newtons) applied by Claire.
View Audio Guided Solution.
Problem 7:
Dexter Eius is walking through the cafeteria when he slips on some spilled milk and falls to the floor. Upon hitting the floor, he skids to a stop with an acceleration of -3.56 m/s/s. Dexter weighs 542 Newtons. Determine the coefficient of friction between Dexter and the floor. Calculate your answer accurate to the third decimal place.
View Audio Guided Solution.
Problem 8:
While decorating her apartment, Julie pushes a 628-N dresser across the floor by applying a 541-N horizontal force. If the coefficient of friction between the dresser and the floor is 0.652, then determine the acceleration (in m/s/s).
View Audio Guided Solution.
Problem 9:
Unbeknownst to most students, every time the school floors are waxed, the physics teachers get together to have a barrel of phun doing friction experiments in their socks (uhm - they have clothes on, its just that they don't have any shoes on their feet). On one occasion, Mr. Lewis applied a horizontal force to accelerate Mr. Smith (mass of 74.8 kg) rightward at a rate of 1.04 m/s/s. If the coefficient of friction between Mr. Smith's socks and the freshly waxed floors is 0.502, then with what force (in Newtons) must Mr. Lewis be pushing?
View Audio Guided Solution.
Problem 10:
A 960-kg car skids to a stop across a road surface which has a coefficient of friction of 0.844 with respect to the tires. Determine the acceleration of the car (in m/s/s).
View Audio Guided Solution.
Problem 11:
Claire deAisles applies a horizontal force of 651 N to accelerate a 57.6-kg supermarket crate. The coefficient of friction between the crate and the floor is 0.736. Determine the acceleration (in m/s/s) of the crate. Calculate your answer accurate to the third decimal place.
View Audio Guided Solution.
Problem 12:
A 27.5-kg object is moving rightward across a horizontal surface with a speed of 13.1 m/s. The coefficient of friction between the object and the surface is 0.492. Determine the time (in seconds) required for the object to stop.
View Audio Guided Solution.
Problem 13:
A 970-kg car moving rightward with a speed of 16.8 m/s skids to a stop in 3.26 seconds. Determine the coefficient of friction between the car tires and the roadway. Calculate your answer accurate to the fourth decimal place.
View Audio Guided Solution.
Problem 14:
Chuck Wagon applies a horizontal force of 679 N to accelerate a 57.4-kg box from a rest position. The coefficient of friction between the crate and the floor is 0.804. Determine the velocity (in m/s) of the crate after 1.22 seconds.
View Audio Guided Solution.
Problem 15:
Albert is attempting to drag his 35.6-kg Golden Retriever across the yard by applying a horizontal force. What force (in Newtons) must be applied to move the dog with a constant speed of .85 m/s? The coefficient of friction between the dog and the ground is 0.554.
View Audio Guided Solution.