Mechanics: Momentum and Collisions
Momentum and Collisions: Audio Guided Solution
Extra Problem 11:
A 2.0-kg mass is given an initial velocity by a spring-loaded mechanism on a frictionless surface. This mass impacts a 3.0-kg mass sitting on the edge of the table. The 2.0-kg mass ends up moving backwards at 1.34 m/s. How far from the base of the 1.22-meter high table does the 3.0-kg mass land (in m)? The spring constant is 344 Newtons/meter and the spring is initially compressed 0.15 meters. TIP: If necessary, you might want to review principles of horizontally-launched projectiles.
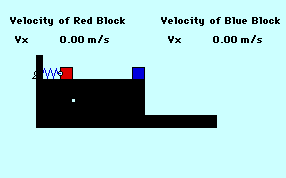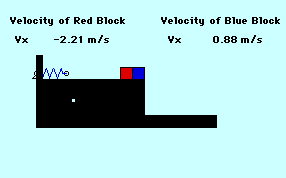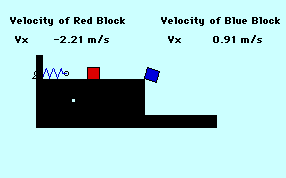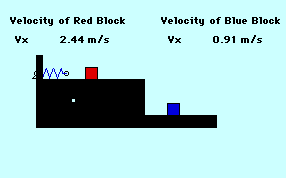
Audio Guided Solution
Read About It!
Get more information on the topic of Momentum and Collisions at The Physics Classroom Tutorial.
Return to Original Problem Set
Return to Index of Extra Problems
Return to Overview
Habits of an Effective Problem Solver
An effective problem solver by habit approaches a physics problem in a manner that reflects a collection of disciplined habits. An effective problem-solver...
-
...reads the problem carefully and develops a mental picture of the physical situation. If needed, they sketch a simple diagram of the physical situation to help visualize it.
-
...identifies the known and unknown quantities in an organized manner, often times recording them on the diagram iteself. They equate given values to the symbols used to represent the corresponding quantity (e.g., vo = 0 m/s; a = 4.2 m/s/s; vf = 22.9 m/s; d = ???.).
-
...plots a strategy for solving for the unknown quantity; the strategy will typically center around the use of physics equations be heavily dependent upon an understaning of physics principles.
-
...identifies the appropriate formula(s) to use, often times writing them down. Where needed, they perform the needed conversion of quantities into the proper unit.
-
...performs substitutions and algebraic manipulations in order to solve for the unknown quantity.