There are three very similar versions of this question. Each version provides a before-after diagram showing the initial and final momentum of an object. Five sets of collision parameters are presented. Two of them, when combined, would cause the specified change of state. This is one of the three versions:
Version 1
For the given pre- and post-collision information, identify the collision parameters that are consistent with the indicated momentum change. Pick two sets of parameters. (A + sign indicates a rightward direction; a - sign indicates a leftward direction.)

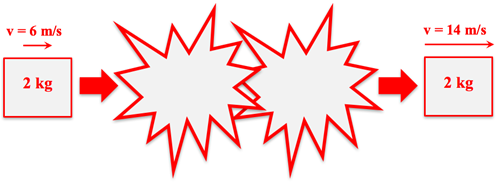
a. Impulse = +8 N•s
b. Impulse = -8 N•s
c. F = +4 N, ∆t = 2 s
d. ∆p = +24 kg•m/s
e. F = + 32 N, ∆t = 0.5 s