As mentioned earlier, a wave is an energy transport phenomenon that transports energy along a medium without transporting matter. A pulse or a wave is introduced into a slinky when a person holds the first coil and gives it a back-and-forth motion. This creates a disturbance within the medium; this disturbance subsequently travels from coil to coil, transporting energy as it moves. The energy is imparted to the medium by the person as he/she does work upon the first coil to give it kinetic energy. This energy is transferred from coil to coil until it arrives at the end of the slinky. If you were holding the opposite end of the slinky, then you would feel the energy as it reaches your end. In fact, a high energy pulse would likely do some rather noticeable work upon your hand upon reaching the end of the medium; the last coil of the medium would displace your hand in the same direction of motion of the coil. For the same reasons, a high energy ocean wave can do considerable damage to the rocks and piers along the shoreline when it crashes upon it.
How is the Energy Transported Related to the Amplitude?
The amount of energy carried by a wave is related to the amplitude of the wave. A high energy wave is characterized by a high amplitude; a low energy wave is characterized by a low amplitude. As discussed earlier in Lesson 2, the amplitude of a wave refers to the maximum amount of displacement of a particle on the medium from its rest position. The logic underlying the energy-amplitude relationship is as follows: If a slinky is stretched out in a horizontal direction and a transverse pulse is introduced into the slinky, the first coil is given an initial amount of displacement. The displacement is due to the force applied by the person upon the coil to displace it a given amount from rest. The more energy that the person puts into the pulse, the more work that he/she will do upon the first coil. The more work that is done upon the first coil, the more displacement that is given to it. The more displacement that is given to the first coil, the more amplitude that it will have. So in the end, the amplitude of a transverse pulse is related to the energy which that pulse transports through the medium. Putting a lot of energy into a transverse pulse will not effect the wavelength, the frequency or the speed of the pulse. The energy imparted to a pulse will only affect the amplitude of that pulse.
Consider two identical slinkies into which a pulse is introduced. If the same amount of energy is introduced into each slinky, then each pulse will have the same amplitude. But what if the slinkies are different? What if one is made of zinc and the other is made of copper? Will the amplitudes now be the same or different? If a pulse is introduced into two different slinkies by imparting the same amount of energy, then the amplitudes of the pulses will not necessarily be the same. In a situation such as this, the actual amplitude assumed by the pulse is dependent upon two types of factors: an inertial factor and an elastic factor. Two different materials have different mass densities. The imparting of energy to the first coil of a slinky is done by the application of a force to this coil. More massive slinkies have a greater inertia and thus tend to resist the force; this increased resistance by the greater mass tends to cause a reduction in the amplitude of the pulse. Different materials also have differing degrees of elasticity. A more elastic medium will allow a greater amplitude pulse to travel through it; the same force causes a greater amplitude.
Energy-Amplitude Mathematical Relationship
The energy transported by a wave is directly proportional to the square of the amplitude of the wave. This energy-amplitude relationship is sometimes expressed in the following manner.
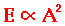
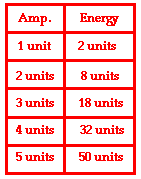 This means that a doubling of the amplitude of a wave is indicative of a quadrupling of the energy transported by the wave. A tripling of the amplitude of a wave is indicative of a nine-fold increase in the amount of energy transported by the wave. And a quadrupling of the amplitude of a wave is indicative of a 16-fold increase in the amount of energy transported by the wave. The table at the right further expresses this energy-amplitude relationship. Observe that whenever the amplitude increased by a given factor, the energy value is increased by the same factor squared. For example, changing the amplitude from 1 unit to 2 units represents a 2-fold increase in the amplitude and is accompanied by a 4-fold (22) increase in the energy; thus 2 units of energy becomes 4 times bigger - 8 units. As another example, changing the amplitude from 1 unit to 4 units represents a 4-fold increase in the amplitude and is accompanied by a 16-fold (42) increase in the energy; thus 2 units of energy becomes 16 times bigger - 32 units.
This means that a doubling of the amplitude of a wave is indicative of a quadrupling of the energy transported by the wave. A tripling of the amplitude of a wave is indicative of a nine-fold increase in the amount of energy transported by the wave. And a quadrupling of the amplitude of a wave is indicative of a 16-fold increase in the amount of energy transported by the wave. The table at the right further expresses this energy-amplitude relationship. Observe that whenever the amplitude increased by a given factor, the energy value is increased by the same factor squared. For example, changing the amplitude from 1 unit to 2 units represents a 2-fold increase in the amplitude and is accompanied by a 4-fold (22) increase in the energy; thus 2 units of energy becomes 4 times bigger - 8 units. As another example, changing the amplitude from 1 unit to 4 units represents a 4-fold increase in the amplitude and is accompanied by a 16-fold (42) increase in the energy; thus 2 units of energy becomes 16 times bigger - 32 units.
Earthquakes and other geologic disturbances sometimes result in the formation of seismic waves. Seismic waves are waves of energy that are transported through the earth and over its surface. Earthquakes are given a Richter scale rating that indicates how intense the earthquake is. Use the Earthquake Energy widget below to explore the relationship between the Richter scale magnitude and the amount of energy transmitted by seismic waves.
Check Your Understanding
1. Mac and Tosh stand 8 meters apart and demonstrate the motion of a transverse wave on a snakey. The wave can be described as having a vertical distance of 32 cm from a trough to a crest, a frequency of 2.4 Hz, and a horizontal distance of 48 cm from a crest to the nearest trough. Determine the amplitude, period, and wavelength of such a wave.
2. An ocean wave has an amplitude of 2.5 m. Weather conditions suddenly change such that the wave has an amplitude of 5.0 m. The amount of energy transported by the wave is __________.
a. halved
b. doubled
c. quadrupled
d. remains the same
3. Two waves are traveling through a container of an inert gas. Wave A has an amplitude of 0.1 cm. Wave B has an amplitude of 0.2 cm. The energy transported by wave B must be __________ the energy transported by wave A.
a. one-fourth
b. one-half
c. two times larger than
d. four times larger than